Understanding Melasma: The Complexities and Misconceptions About Treatment
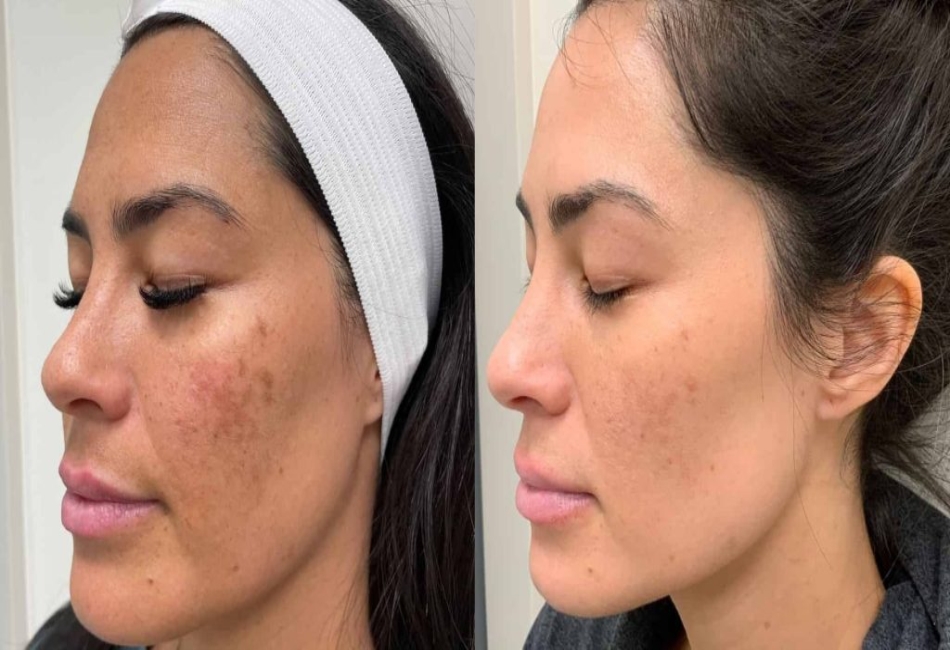
Melasma is a common and bothersome skin condition that affects many people worldwide. People with melasma often have dark spots on their faces. The condition can have a significant effect on their self-esteem and confidence. Although it is usually associated with changes in hormone levels, melasma can also be triggered by several other factors, including sun exposure, pregnancy, and certain medications. In the pursuit of clear, even-toned skin, many individuals turn to lasers as a quick solution for reducing the appearance of melasma. However, recent discussions have raised concerns that laser treatments may not always be the best option, and in some cases, they could even worsen the condition.
What is Melasma?
A skin condition called melasma, characterized by the presence of brown or gray-brown patches of pigmentation, typically appears on the face. The condition tends to affect women more than men, particularly during periods of hormonal changes, such as pregnancy, birth control use, or hormone replacement therapy. However, melasma can also occur in men, especially when overproduction of melanin leads to the pigmentation characteristic of melasma. This overproduction can occur due to several factors, such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, hormonal imbalances, and genetic predisposition. As a result, melasma typically manifests as dark patches on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and nose, though it can also appear on the neck, forearms, and other exposed areas.
Common Causes of Melasma
Melasma is primarily caused by three main factors: hormonal fluctuations, sun exposure, and genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal Changes: An essential factor in the development of melasma, which is why many women experience this condition during pregnancy, is also known as the “mask of pregnancy.” Using hormone replacement treatment or oral contraceptives as a method of abortion can also trigger melasma due to the hormonal fluctuations that occur.
- Sun Exposure: The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a well-known trigger for the development of melasma. The sun stimulates melanocytes in the skin, leading to an overproduction of melanin. Prolonged exposure to sunlight without protection can exacerbate or trigger melasma for the first time.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. If melasma runs in the family, it may be more challenging to prevent or treat.
How Melasma Is Diagnosed
Melasma is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, with the assistance of a dermatologist, who evaluates the patient’s medical history and the appearance of their skin. In some cases, a Wood’s lamp may be used to help determine the depth of pigmentation (epidermal or dermal). Epidermal melasma is more easily treated with topical treatments, whereas dermal melasma may require more extensive treatments and a longer duration to achieve improvements.
Why Laser Treatment Is Not Always the Best Solution for Melasma
While lasers are often promoted as a solution for many skin concerns, including pigmentation disorders like melasma, recent discussions, such as those shared by skincare experts, have revealed that laser treatments can sometimes worsen the condition. For individuals with melasma, especially those with deep or hormonal-related pigmentation, lasers might not be the right treatment choice.
One of the primary concerns about laser treatment for melasma is that it may cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). When the skin becomes darker, this situation often occurs due to soreness or inflammation, which can result from undergoing harsh laser treatments. Many people have reported that laser treatment has worsened their melasma, and this is becoming a growing concern within the dermatology community.
For this reason, a melasma treatment plan should be approached with caution. While lasers can be effective for certain types of pigmentation, their use in treating melasma should be carefully considered by a trained and experienced professional. Non-invasive or combined treatments may be more effective in controlling melasma without risking future damage.
The Role of Sunscreen in Managing Melasma
Sun safety is essential for controlling melasma. Even short periods in the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays can exacerbate color, which is what causes melasma flare-ups in the first place. To keep melasma under control, use a sunscreen that protects against the sun’s rays and has an SPF of 30 or higher. (ideally 50) Every day.
Additionally, avoiding direct sunlight, especially during peak hours, can also be beneficial. Wearing hats and sunglasses can shield you from the sun from 10:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. Chemical sunscreens may not function as effectively for patients with melasma as titanium dioxide or zinc oxide.
Effective Treatments for Melasma
For individuals seeking to manage their melasma, A variety of treatments are available, depending upon the severity of the condition. And the underlying cause of the pigmentation.
- Topical Treatments: These are often the first line of defense in treating melasma and include components such as kojic acid, hydroquinone, retinoids, and azelaic acid. These ingredients help to lighten hyperpigmented areas and slow down melanin production.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels can exfoliate the skin and help remove the outer layers of pigmented skin. These are typically used in conjunction with other treatments for more noticeable results.
- Microneedling: Using tiny needles to create small skin holes, this procedure increases collagen production and improves pigmentation over time. Melasma can be treated with microneedling when done correctly.
- Prescription-Only Medications: A dermatologist may recommend oral or stronger topical medications to treat the underlying causes of melasma, such as hormonal imbalances.
- Laser Treatment: While lasers can sometimes be effective, they should be used with caution. Non-ablative lasers, which stimulate collagen production without removing the skin’s outer layers, are preferred over more invasive options for treating melasma.
Preventing Melasma from Worsening
In addition to staying out of the sun every day, making the following changes to your lifestyle can help keep melasma from getting worse:
- Limit Hormonal Fluctuations: For women, avoiding oral contraceptives or hormonal therapies that may trigger melasma is essential. If melasma is related to pregnancy, it typically resolves on its own after delivery.
- Avoid Skin Irritation: Harsh skincare products or over-exfoliating can irritate the skin and worsen melasma. Use mild skincare products and avoid harsh skin care products and aggressive treatments unless recommended by a dermatologist.
- Diet and Hydration: Eating a healthy diet, increasing your water intake, and consuming meals high in antioxidants can help your skin look and feel better from the inside out.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
Melasma is a challenging condition that requires a personalized and comprehensive treatment plan. Laser treatments for melasma should be used with caution, and non-invasive methods may be more effective. If you know what causes melasma and treat it properly, you can get skin that is healthy and more evenly toned.
Over time, melasma improves. Be patient, follow the doctor’s instructions, and endure until you get healthier skin. Laser treatments may be effective, but they can worsen the condition. Melasma specialists can create a customized treatment plan for you, so it is recommended that you seek their help.
Harmony Aesthetics Clinic
1 Grange Road, #13-01
Orchard Building,
Singapore 239693
Tel: 6970 5418
Whatsapp: 8822 3089